8 Things In Chocolate Edibles That Make Your High Different
Chocolate is a unique bit of food that for the last 4,000 years, has been a part of our various cultures and history. Today we see chocolate edibles infused with cannabinoids, and people have been starting to realize that the buzz is different.
Why do chocolate edibles have a different high?
Here are 5 things in Chocolate that make your high different!
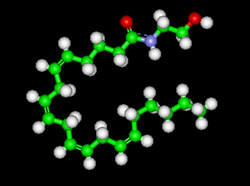
ANANDAMIDE — C22H37NO2
also known as: N-arachidonoylethanolamine or AEA,
Molecular Mass 347.53 g/mol
Chocolate contains small quantities of anandamide, an endogenous cannabinoid found in the brain. Anandamide is a neurotransmitter that targets the same brain structures as THC, the active ingredient in cannabis. But to make a substantial impact on the brain’s own natural anandamide levels, experts estimate you would need to eat several kilos of chocolate! Neuroscientist Daniele Piomelli suggests that chocolate works more indirectly to produce its high’. As well as anandamide itself, chocolate contains two chemicals known to slow the breakdown of anandamide. Chocolate might therefore work by prolonging the action of this natural stimulant in the brain.
Now imagine how the entourage effect will be applied here. The rule is the more cannabinoids and terpenes that you have present, the stronger the effects of each. To this note, I’d like to say that I much prefer the term Ensemble, where not just one cannabinoid or terpene is being boosted, so much as all of them are being boosted by one another.
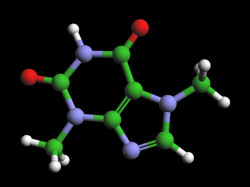
THEOBROMINE – C7H8N4O2
formerly known as xantheose,
Molecular Mass 180.164 g/mol
Theobromine is a stimulant frequently confused with caffeine. Theobromine affects humans similarly to caffeine, but on a much smaller scale. Theobromine is mildly diuretic (increases urine production), is a mild stimulant, and relaxes the smooth muscles of the bronchi in the lungs. In the human body, theobromine levels are halved between 6-10 hours after consumption. Because of its ability to dilate blood vessels, theobromine also has been used to treat high blood pressure. Theobromine has very different effects on the human body from caffeine; it is a mild, lasting stimulant with a mood-improving effect, whereas caffeine has a strong, immediate effect and increases stress. A normal portion of chocolate exhibits psychopharmacological activity.
Given Theobromine’s ability to increase blood flow, dilate blood vessels, and create a caffeine-like experience without an instant and sometimes stressful or anxious onset, and then combine that with the THC. To some extent you have to come to realize that these molecules are now moving through your body at a quicker speed overall. Better, faster delivery!
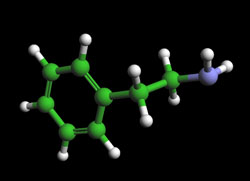
PHENYLETHYLAMINE – C8H11N
also known as ß-phenylethylamine (ß-PEA) and 2-phenylethylamine
Molecular Mass 121.18 g/mol
Phenylethylamine has earned the nickname ‘chocolate amphetamine.’ High levels of this neurotransmitter help promote feelings of attraction, excitement, giddiness, and apprehension. Phenylethylamine works by stimulating the brain’s pleasure centers and reaches peak levels during orgasm. Chocolate has the highest concentration in any food of phenylethylamine, which is the chemical produced in the brain when a person is in love. Yet the role of the “chocolate amphetamine” is disputed. Most if not all chocolate-derived phenylethylamine is metabolized before it reaches the CNS. Some people may be sensitive to its effects in very small quantities.
Much like the energy boost that is given from the theobromine, the phenylethylamine will give your excited self that feeling of.. well.. how else can you describe the most perfect moment of perpetual existence seemingly freezing in time other than at the peak of orgasm? While the presence of this in chocolate is not enough to really trigger this much very much, but even just a little is enough to provide an interesting backdrop to the feelings that cannabinoids bring to the table already!
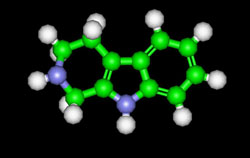
TETRAHYDRO-BETA-CARBOLINE – C11H12N2
also known as Tryptoline and and tetrahydronorharmane
Molecular Mass– 172.2264
Cacao and chocolate bars contain a group of neuroactive alkaloids known as tetrahydro-beta-carbolines C(THbetaCs). Tryptolines are also potent reuptake inhibitors of serotonin and epinephrine, with significantly greater selectivity for serotonin. Tetrahydro-beta-carbolines are also found in beer, wine, and liquor; they have been linked to alcoholism. But the possible role of these chemicals in chocolate addiction remains unclear.
It can be lightly drawn from the presence of tetra-hydro-beta-carboline is a part of why we cannot stop thinking about chocolate!
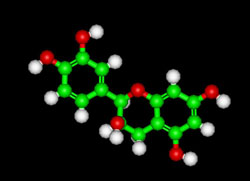
EPICATECHIN– C30H26O13
also known as epi-Catechin
Molecular Mass–290.3
Cocoa, especially dark chocolate, has high amounts of the flavonoid Epicatechin and has been found to have nearly twice the antioxidants of red wine and up to three times those found in green tea. Epicatechin may improve blood flow and may have potential applications for cardiac health. Two recent clinical trials have found that cocoa flavanols can boost the flow of blood to key areas of the brain, giving scientists hope for developing treatments for dementia and strokes. Another study found potential applications for treating blood circulation problems associated with long-term diabetes.
Recent studies have shown that cocoa or dark chocolate has potent health benefits for people. Dark chocolate is full of the flavonoids epicatechin and gallic acid, which are antioxidants that help protect blood vessels, promote cardiac health and prevent cancer. It also has been effectively demonstrated to counteract mild hypertension. In fact, dark chocolate has more flavonoids than any other antioxidant-rich food such as red wine, green and black tea, and blueberries. There has even been a fad diet named the “Chocolate Diet” that emphasizes eating chocolate & cocoa powder in capsules. However, consuming milk chocolate or white chocolate, or drinking milk with dark chocolate appears to largely negate the health benefits. Chocolate is also a calorie-rich food, with a high content of saturated fat, so daily intake of chocolate also requires reducing caloric intake of other foods. See: “Cocoa Has More Phenolic Phytochemicals and a Higher Antioxidant Capacity than Teas and Red Wine.”
We already know that cannabinoids are awesome at anti-inflammation, so when we add this particular player onto the field, we have a whole new scope of possibilities within our already broad targetable areas of interest!
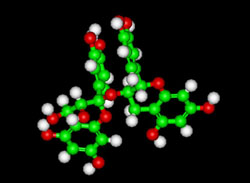
PROCYANIDIN – C15H14O6
Molecular Mass-594.5196 g/mol
Procyanidins are members of the class of proanthocyanidin (or condensed tannins) flavonoids. They are oligomeric compounds, formed from catechin and epicatechin molecules. Data from a short-term investigation support the concept that certain food-derived flavonoids can favorably alter eicosanoid synthesis in humans, providing a plausible hypothesis for a mechanism by which they can decrease platelet activation in humans. Chocolate procyanidins decrease the leukotriene-prostacyclin ratio in humans and human aortic endothelial cells (See Abstract)
While most of this will read to be a completely different language, it can be lightly drawn that the presence of Procyanodin and Epicatechin is a unique operator and while it isn’t immediately clear as to how the two interact or if they interact at all, the mere presence of this is at least beneficial with our without the interaction.
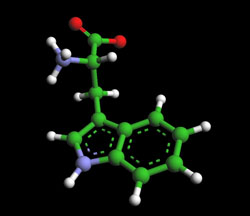
TRYPTOPHAN – C11H12N2O2
Molecular Mass-204.225 g/mol
Tryptophan is a chemical that the brain uses to make a neurotransmitter called serotonin. High levels of serotonin can produce feelings of elation, even ecstasy.
It’s easy to see that chocolate with any amount of THC can double up on these types of feelings!
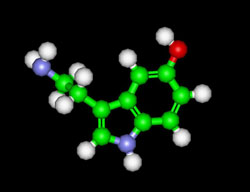
SEROTONIN – C10H12N2O
Also known as: 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)
Molecular Mass-176.215 g/mol
Serotonin is present both in cocoa powder and in dark chocolate. The levels of serotonin in chocolate samples containing 70–100% cocoa ranged from 1.30 to 2.93 mg/kg.
The majority of the body’s serotonin, between 80-90%, can be found in the gastrointestinal tract. Serotonin that is used inside the brain though must be produced within it.
That is likely why the edibles that you are consuming may be able to contain large amounts of serotonin, however, the sleepiness contained therein are not readily able to be taken into the brain, though it does stand to note that people with lower levels of serotonin are often depressed or anxious, whereas those with higher levels are able to regulate those moods. It is also speculated that serotonin interacts with the part of the brain that makes you go to sleep, or become awake, though whether you feel one way or the other depends on the side that is stimulated and which receptors are used.
Serotonin Functions – Healthline
Meet the Molecules in Chocolate: Informal Opportunities for Building Thematic Molecular Models with Children –Journal of Chemical Education
The Science of Chocolate: Interactive Activities on Phase Transitions, Emulsification, and Nucleation
Anandamide – the ‘bliss’ molecule-
Anandamide – Brain Activity and Functions
Tetrahydro-ß-carbolines, Potential Neuroactive Alkaloids, in Chocolate and Cocoa



